Quickstart
Tip
If you're want to quickly see what Contember can do, check out our Headless CMS template. It's the easiest way to try out what Contember can do in minutes.
Create new project with Contember#
In this tutorial we will show you how to setup both Contember Engine and Contember Admin to create your first project.
Prerequisites
- Installed NPM version 7+
- Installed Docker with Docker Compose
It will create a new folder with basic Contember setup. After it is done:
And then install dependencies:
- Mac
- Windows
- Linux or WSL
note
On Mac we recommend to install dependencies directly in Docker - not by running npm install directly but as shown above.
Use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
If you are using Windows we recommend using Windows Subsystem for Linux if possible. Some features might not work correctly without it (such as rebuilding automatically after a file change).
On Windows we recommend to install dependencies directly in Docker.
And you're ready to go. Just start Docker containers and Contember will be running.
Now, administration UI should be running on address http://localhost:1480.
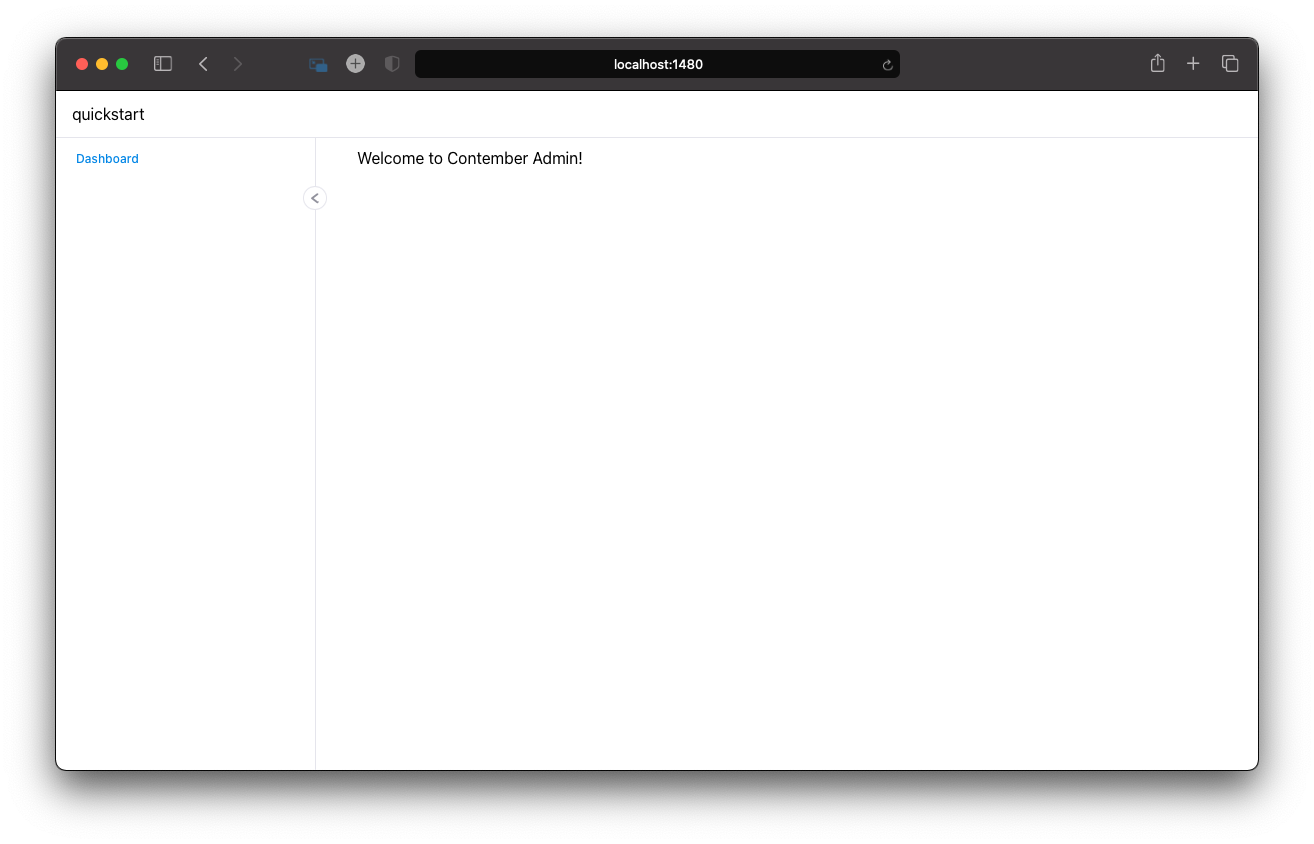
Started services
- Admin UI at http://localhost:1480
- API endpoints at http://localhost:1481 (you can authorize with token
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000)
For advanced use-cases there is also:
- Adminer database management tool at http://localhost:1485.
- Minio local S3 provider at http://localhost:1483 (you can sign in with contembeer / contember credentials).
- Mailhog testing SMTP at http://localhost:1484.
- PostgreSQL database at localhost:1482 (you can sign in with contember / contember credentials).
Create first project#
From the first step you should have a folder structure that looks like this:
Create your first data model#
First you have to tell Contember Engine, how your data model looks like. The init command automatically created api/model/index.ts file, so go there.
Here you start defining your project schema. Really simple example looks like this:
- Import
SchemaDefinitionso you'll get TypeScript autocompletion. - Define your fist entity -
Article. For this example let's just add two columns namedtitleandcontent, both arestring.
Then you need to generate a database migration for Contember Engine:
Contember CLI
npm run contember is a Contember CLI, if you call this command you'll see all the available commands.
We'll use migrations:diff command. It goes through your schema and generates migration - instructions for Contember how to get from previous state to your new one.
This command needs two parameters: first is name of your project (quickstart in our example) and then name your migration. It can be anything you want.
Run this command and choose an option Yes and execute immediately. It will create your migration and after confirmation execute it. Now if you would look into your database, you would see there a table article with three columns: id, title, content. Nice.
Create your administration UI#
Now we have something we want to edit in UI. Let's start by adding a listing page for our articles.
Add listing page#
Go to admin/pages and create new file Articles.tsx.
- Import
@contember/adminpackage for TypeScript autocompletion. - Export new
ArticleList(you can name it anyway you like) - Use
TablePagecomponent to show the data in a simple table. - Tell it which entities you'd like to edit. In our case it's
Article(it has to be the same name we used in the model). - Name your list (
pageName="article"). Name is used for url in administration. - Tell it what data you want to see. We'll want to see
titlein our example. (And added it intoTableCellwhich we'll make use of later.)
If you go to localhost:1480/articles you'll see list of your articles. Which is empty as we didn't add any data there yet.
Let's add some data.
Add create page#
- For simplicity we'll add it to the same file.
- This time we'll use
CreatePagecomponent. - We'll tell it what we want to add (
Article), how is this component named (articleNew). - We'll use two new components -
TextFieldandTextAreaFieldand tell them what fields to edit.
Now at localhost:1480/article-new you can create new article. And if you go to the list of articles you'll see the data are there.
But it doesn't work very well. One of the things missing is to go to edit mode after you created a new article. So let's start by adding an edit page:
Add edit page#
For simplicity we'll add it to the same file as well. It looks almost the same as the create page - but we have to tell it which article to edit:
Let's use it. We'll redirect users from our create page to the edit page after the article is successfully created:
We added two new things: rendererProps and redirectOnSuccess:
rendererPropsare pretty simple in this case: just added title so we know that we're on this page,redirectOnSuccessis more complicated: we take user topagewith id of the newly created page.
Now if you create a new article you're automatically redirected to the edit page.
What's missing is an edit button in the list of pages.
- We've added new
TableCelland into it aPageLinkByIdcomponent. - This component is pretty simple - it will create a link to a component called
articleand sends id as parameter. Which is actually our edit page. - Minor touch is use of
shrunkwith tells the cell to be as small as possible.
Add pages to side menu#
One last thing is to add our pages to the left sidebar:
And that's it! You have just created a simple data model and created custom interface, so you can edit the data. If you want you can fetch the data via GraphQL API that was created in the background you can read more in Content API topic.